
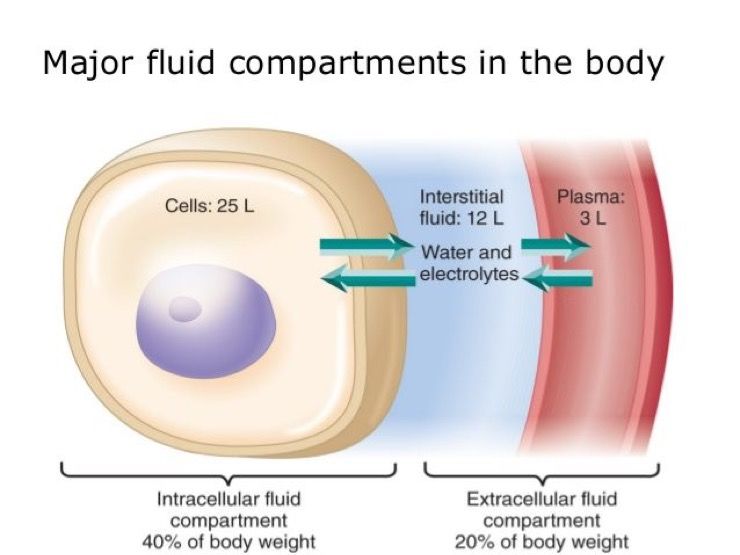
The lymph contained in the lymphatic vessels, which circulates between tissues and blood.The interstitial or tissue fluids, which bathe the cells and circulate slowly.This milieu is formed by the extra cellular fluids, i.e. Muticellular organisms are surrounded by an external environment- air or water- but their cells live in a fluid environment which Claude Bernard in 1878 named the “milieu interior” (internal environment). When blood coagulates, it first becomes solid clot and then a fluid oozes out from clot, which is called the serum. Blood is made up of a liquid, the blood plasma, in which ells (erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets) and minute particles are suspended. Between these last two compartments the exchange of diffusible substances is easy and continuous, so they have a similar content of water and salts. One is within the cells, the intracellular fluid and the other two, outside the cells and forming the extra cellularfluid and includes interstitial fluid and blood plasma. 36 (2):259-273.The body fluids are distributed in three compartments. Evaluation and Management of Dehydration in Children. Comparison between oral versus intravenous rehydration to treat dehydration in pediatric gastroenteritis.

Evidence-based emergency medicine/systematic review abstract. Oral Ondansetron in Management of Dehydrating Diarrhea with Vomiting in Children Aged 3 Months to 5 Years: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Vol 3: 2623-34.ĭanewa AS, Shah D, Batra P, Bhattacharya SK, Gupta P. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. Infectious diarrheal disease and dehydration. American Academy of Pediatrics, Provisional Committee on Quality Improvement, Subcommittee on Acute Gastroenteritis. Practice parameter: the management of acute gastroenteritis in young children. Antiemetics for reducing vomiting related to acute gastroenteritis in children and adolescents. 149(5):726.Īlhashimi D, Alhashimi H, Fedorowicz Z. Oral ondansetron decreases the need for intravenous fluids in children with gastroenteritis. Effect of Dilute Apple Juice and Preferred Fluids vs Electrolyte Maintenance Solution on Treatment Failure Among Children With Mild Gastroenteritis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. įreedman SB, Willan AR, Boutis K, Schuh S. Fruit Juice in Infants, Children, and Adolescents: Current Recommendations. Heyman MB, Abrams SA, SECTION ON GASTROENTEROLOGY, HEPATOLOGY, AND NUTRITION., COMMITTEE ON NUTRITION. Oral ondansetron for gastroenteritis in a pediatric emergency department. Oral versus intravenous rehydration of moderately dehydrated children: a randomized, controlled trial. Spandorfer PR, Alessandrini EA, Joffe MD, Localio R, Shaw KN. The BUDDY (Bedside Ultrasound to Detect Dehydration in Youth) study. Jauregui J, Nelson D, Choo E, Stearns B, Levine AC, Liebmann O, et al. Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine. Pediatric vascular access and blood sampling techniques. Usefulness of the serum electrolyte panel in the management of pediatric dehydration treated with intravenously administered fluids. Managing acute gastroenteritis among children: oral rehydration, maintenance, and nutritional therapy. Pediatric diabetic ketoacidosis, fluid therapy, and cerebral injury: the design of a factorial randomized controlled trial.
Glaser NS, Ghetti S, Casper TC, Dean JM, Kuppermann N. Singhi SC, Shah R, Bansal A, Jayashree M. Neurologic sequelae after treatment of severe hyponatremia: a multicenter perspective. Sterns RH, Cappuccio JD, Silver SM, Cohen EP. Language guiding therapy: the case of dehydration versus volume depletion.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
